Any time you’re applying heat to food, there’s science going on, including when you’re grilling. Grilled food tastes as good as it does in large part due to the Maillard reaction, a chemical process that takes place when heat comes together with amino acids and sugars. Understanding the Maillard reaction can help you to get better at grilling and produce tastier meals.
What Is the Maillard Reaction?
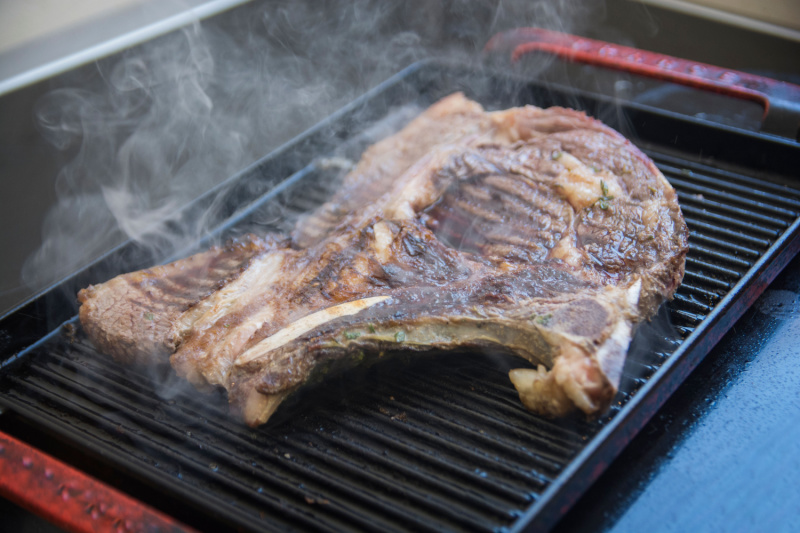

The Maillard reaction is a process in which the heat of the grill, oven, burner, or other heat source causes a chemical reaction between the proteins and sugars present in the food being cooked. Almost any food that contains protein and sugar can undergo the Maillard reaction when it is cooked, though it’s most often thought of in the context of grilling meat.
Who Discovered It?

The Maillard reaction is named for its discoverer, Louis-Camille Maillard, a French chemist who described this process in 1912. At the time, he was doing medical research, exploring what happened when heat was applied to food in an effort to better understand and treat diabetes.
How Does the Maillard Reaction Happen?
When heat is applied to amino acids and sugar, the molecules break down and recombine, creating a compound called glycosylamine. The glycosylamine is unstable, so it rearranges itself as it’s heated in the oven or on the grill, creating more stable compounds called ketosamines. The ketosamines then undergo further reactions to form a variety of substances, some of which have different flavors and aromas. Melanoidins, compounds that are brown in color, are also created in this process.
How Does it Affect the Food Being Cooked?
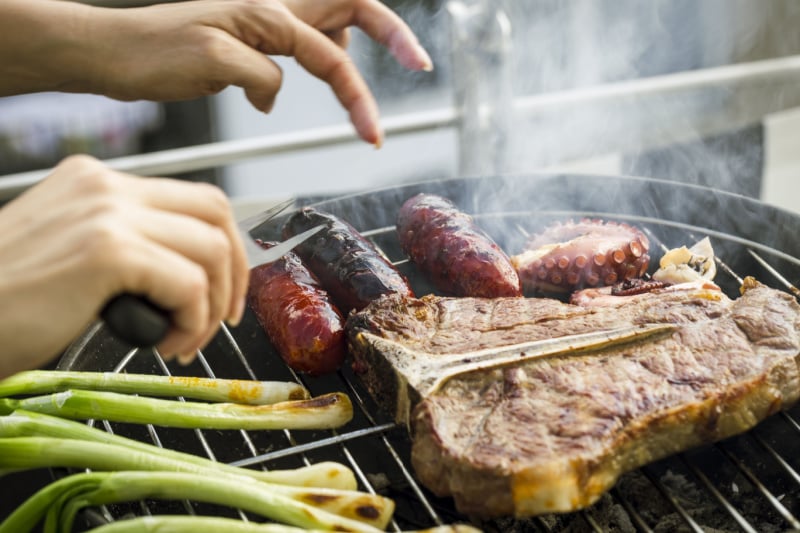

The Maillard reaction enhances the flavor and color of foods. Through this chemical reaction, the food being cooked becomes brown, and hundreds of flavor compounds are created that make the flavor of the food deeper and more complex. The Maillard reaction is also what makes foods like roasting coffee, steaks on the grill, and bread baking in the oven smell so good as they cook. It also forms a crust on the outside of the food that adds textural contrast.
Does Browning Indicate That the Maillard Reaction Has Happened?
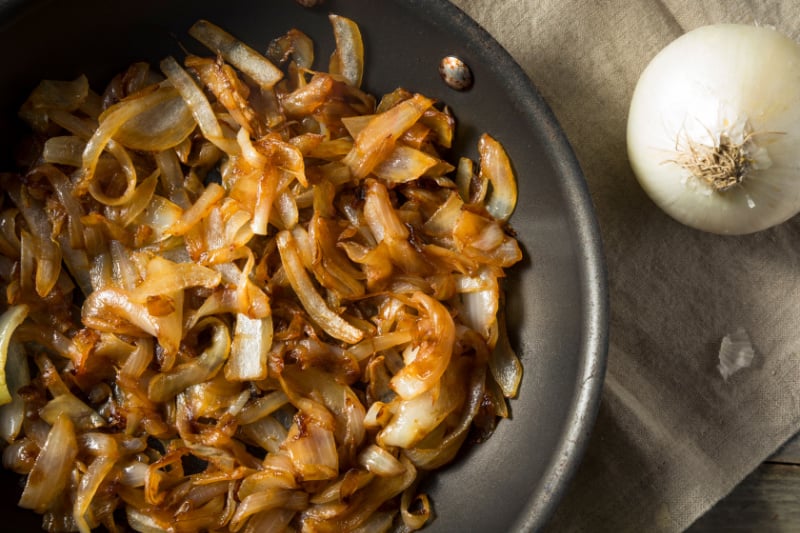

Browning of food being cooked is often caused by the Maillard reaction, but that’s not always the case. Foods that are low in protein will typically not undergo this reaction. Sugary foods such as fruits can instead undergo caramelization when they are cooked. When sugar caramelizes, the water cooks off and the sugar breaks down, creating a sweet and sometimes nutty flavor and a brown color.
Additional Resources
- An Introduction to the Maillard Reaction: The Science of Browning, Aroma, and Flavor
- Maillard Taught Us Why Our Food Tastes Better Cooked
- The Marvelous Maillard Reaction
- Five Things Everyone Should Know About the Maillard Reaction
- What Is the Maillard Reaction?
- The Maillard Reaction Is Why Browned Food Tastes So Good
- Maillard Reactions Change the Taste of Your Food
- Understanding the Maillard Reaction
- The Maillard Reaction Explained
- Why Does Food Taste Better When it’s Browned?
- The Difference Between the Maillard Reaction and Caramelization
